What is Blockchain and How Does it Work
Introduction
If you’ve heard of Bitcoin, you’ve heard of blockchain. But blockchain is more than just the technology behind cryptocurrencies. It’s a groundbreaking innovation that’s changing how we record, store, and verify information. This guide breaks it down simply for beginners in 2025.
What is Blockchain?
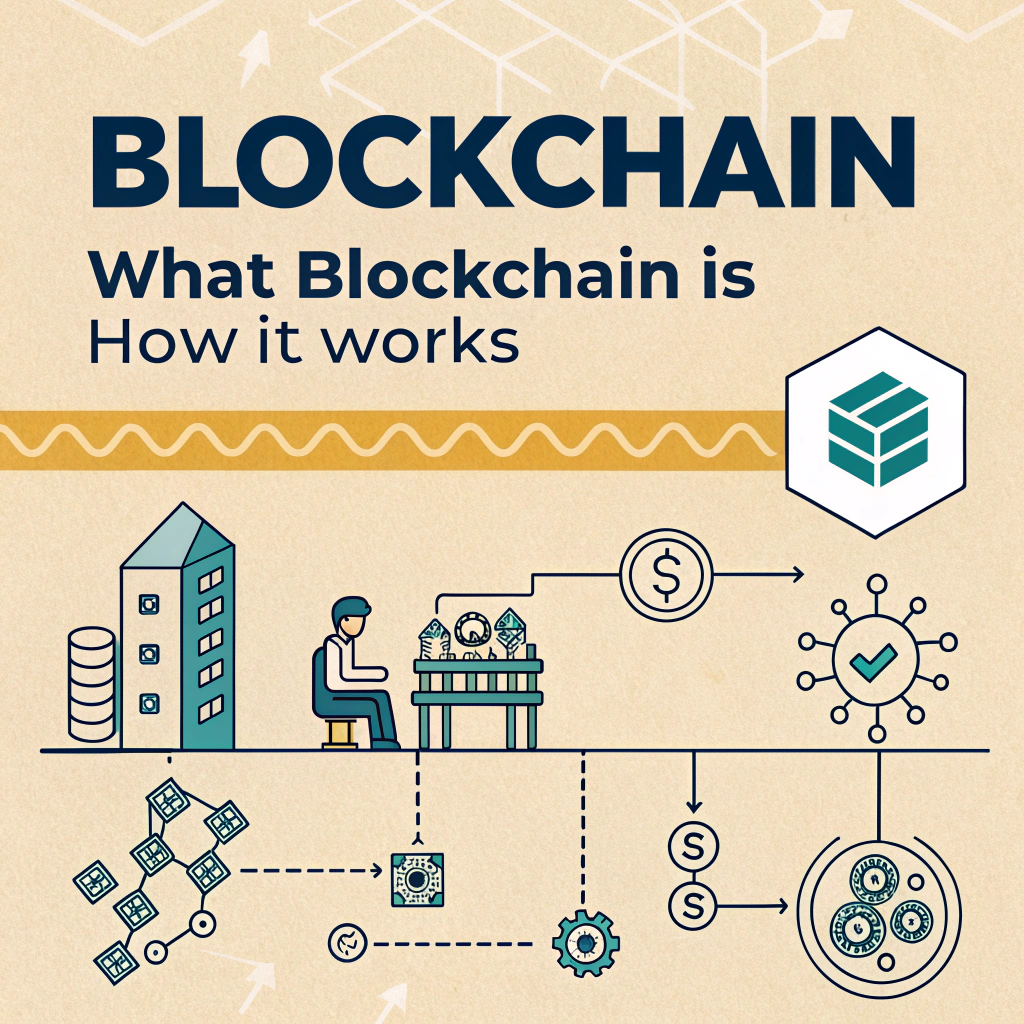
A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Once data is recorded in a blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter, making it ideal for secure, transparent record-keeping.
In simpler terms, it’s like a shared database that everyone can see, but no one can secretly change.
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain operates through a series of “blocks” linked together in chronological order. Each block contains:
- A list of transactions
- A timestamp
- A cryptographic hash of the previous block
These blocks form a chain — hence the name “blockchain.” Every new transaction is verified by network participants (called nodes) before being added to the chain.
Key Components of a Blockchain
- Blocks: Containers of data (transactions).
- Nodes: Computers that maintain the blockchain.
- Miners/Validators: Participants who verify transactions.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Methods for agreement, like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
- Hashing: Ensures data integrity through cryptography.
Types of Blockchains
- Public Blockchains: Open to anyone. (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
- Private Blockchains: Restricted access, used by businesses.
- Consortium Blockchains: Controlled by a group of organizations.
- Hybrid Blockchains: Mix of public and private elements.
Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to anyone | Restricted access |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Security | High (but slower) | Moderate (but faster) |
| Example | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Hyperledger, Quorum |
What Makes Blockchain Secure?
Blockchain security is based on three principles:
- Decentralization: No central point of failure.
- Immutability: Once data is added, it can’t be changed.
- Cryptography: Every block is linked with a secure cryptographic hash.
Together, these make it extremely hard for hackers to manipulate the network.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Crypto
While blockchain is best known for enabling Bitcoin, its use goes far beyond digital currencies:
- Supply Chain Tracking: Track goods in real time with transparency.
- Voting Systems: Secure, tamper-proof elections.
- Healthcare: Secure patient data sharing.
- Real Estate: Faster, fraud-proof property transactions.
- Digital Identity: Self-sovereign identity management.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
- Transparency
- Security
- Reduced need for intermediaries
- Faster transactions
- Lower costs in the long run
- Immutable records
These advantages make blockchain a valuable solution in various sectors like finance, logistics, and even entertainment.
Limitations and Challenges
- Scalability: Networks like Bitcoin are slower compared to traditional systems.
- Energy Consumption: Especially in Proof of Work systems.
- Regulation: Still evolving in many countries.
- Complexity: Hard for non-tech users to understand and adopt.
- Storage: Blockchains can grow large and require significant resources.
Blockchain in 2025: Trends to Watch
- Wider adoption of Proof of Stake for energy efficiency
- Governments experimenting with Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- More enterprise-grade private blockchains
- Interoperability: Blockchains talking to each other
- AI + Blockchain: Smart data automation
Blockchain is evolving beyond theory — it’s becoming infrastructure.
FAQ
Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
No. Bitcoin is one use case of blockchain. Blockchain is the underlying technology.
Can blockchains be hacked?
It’s extremely difficult due to decentralization and cryptography, but vulnerabilities can still exist in apps or poorly built systems.
Do I need to understand coding to use blockchain?
Not at all. Many blockchain apps today are built to be user-friendly for non-technical users.
Will blockchain replace banks?
Not likely replace, but it may force them to modernize and become more transparent.
Conclusion
Blockchain is one of the most disruptive technologies of our time. From finance to supply chains, its potential is massive. As a beginner in 2025, understanding how blockchain works is a key step toward understanding the future of digital systems — and your place in it.